Glossary
ADEME: The French Environment and Energy Management Agency is one of the French partner. It is the coordinator of the project.
Carbon footprint of organisation: It is an estimate measure of the total greenhouse gas emissions produced directly and indirectly by an organisation due to its activities.
Carbon neutral: It consists on having a zero net carbon footprint by reducing greenhouse gas emissions utmost and offset the minimum emissions leftovers with carbon sequestration.
CRES: The Centre for Renewable Energy Sources is the Greek partner. CRES is a public entity active in the fields of renewable energy sources and energy saving.
Ecoinnovazione: It is a start-up consultancy firm which offers innovative advanced services related to the analysis of environmental impacts of products, services and systems, according to a life cycle perspective. It is one of the two Italian partners, with ENEA.
EIHP: Energy Institute Hrvoje Pozar, is the Croatian partner. The institute’s scope of activity is the energy development in the European Union and Croatia until 2050.
ENEA: The Italian National Agency for New Technology, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development is one of the largest scientific and technological state-owned Italian institutions with a specific mission in applied research activities, technology transfer and dissemination of innovation ito companies. It is one of the two Italian partners, with Ecoinnovazione.
Emission factor (EF): A factor establishing the linking between activity data and greenhouse gas emissions produced (cf. part What is an emission factor?).
Emissions (quota) trading system: It is a system in which companies receive or buy emission allowances and can trade these allowances with one another as needed.
Environmental Product Declarations: It is a document that communicates verified, transparent and comparable information about the life-cycle environmental impact of products.
GHG Protocol: This acronym means Greenhouse Gas Protocol. It was developed in partnership with businesses, NGO and governments in order to create a common framework for accounting and reporting. The GHG Protocol provides standards, guidance, tools and training to measure and manage climate-warming emissions.
HOI: The Hermann Otto Institute is the Hungarian partner of the project. Its main fields of activity are environmental monitoring, statuts assessment, policy and strategy preparation, regulation and impact assessment.
IFC: Institut de Formation Carbone is a french based training organisation specialised on climate change and energy themes. It is one of the French partner.
Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change (IPCC): It is an international scientific body working on climate change fields. The role of IPCC is to assess information (scientific, socio-economic, technologic) allowing to understand risks of human activity as the main source of climate change.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO): It is a non-governmental organization which produces international standards related to product, services and systems.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): This methodology allows to determine the environmental impact (energy and materials used, wastes released) of a product, material, process or activity throughout its lifespan.
Life Cycle Inventory analysis (LCI): It represents the second step: the data collection, in the life cycle assessment procedure. LCI consists in accounting in detailed all flows in and out of the studied system (raw materials, energy by type, water, etc).
OECD: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development mission is to promote policies that will improve the economic and social well-being of people around the world.
OEF: The Organisation Environmental Footprint is a methodology to measure environmental impacts of organisations based on a life cycle approach.
PAS 2050: Publicly Available Specification is specification for quantifying the life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of goods and services.
PEF: The Product Environmental Footprint is a methodology to measure and communicate the life cycle environmental performance of products.
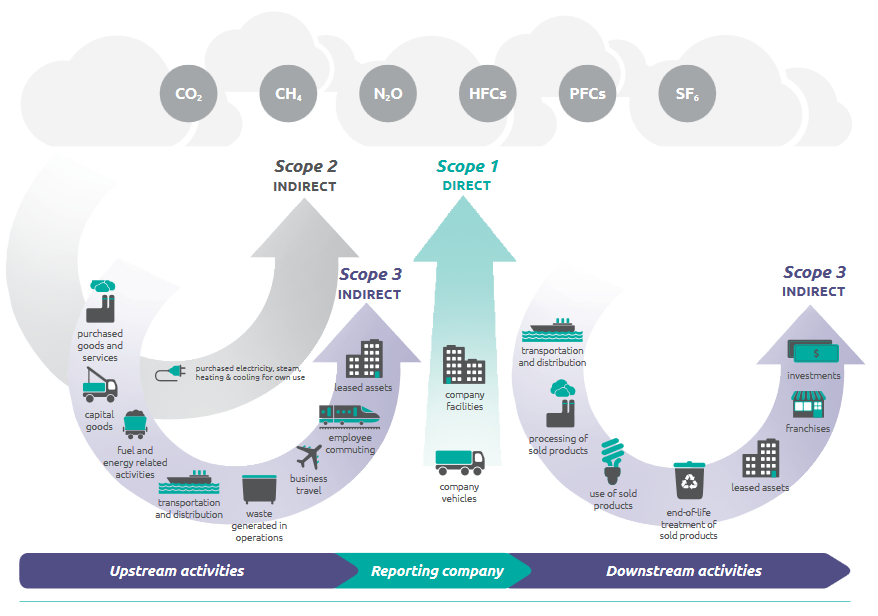
Scopes: we distinguish 3 scope of emissions related to their place of production regarding the organization:
- Scope 1 or direct GHG emissions: In the first scope, the emissions come from sources that are owned or controlled by the reporting company.
- Scope 2 represents energy indirect GHG emissions: these emissions come from the production of purchased energy used by the organization (electricity, heat or steam).
- Scope 3 include other indirect GHG emissions like emissions from business travel by employees, transport of products and materials,etc.pe, they are emissions produced by the organization directly.
Uncertainty: It is a probabilistic measure of the level of confidence of the result which can be affected by the degree of agreement in the scientific studies considered (quality, type, amount). (cf part What is an emission factor? → Uncertainty)